Most distant star in the universe is spotted - 28 billion light years away
Scientists have seen the most distant
ever, a million times as bright as our sun, 28 billion light years away.
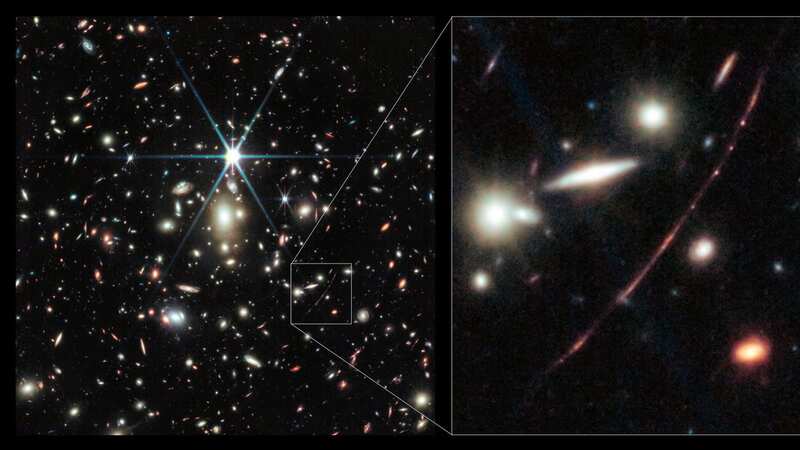
Light from the star, Earendel, has taken 12.9 billion years to reach the lens of the James Webb Space Telescope. With the universe constantly expanding, scientists have calculated that Earendel is by now 28 billion light years away from us.
Earendel, in the Sunrise Arc galaxy, is a type-B star, Webb’s Near-Infrared Camera shows. That puts it at 10-20,000 C, more than twice as hot as our sun Sol. It was observable due to the gravitational lensing phenomenon – a cluster of galaxies between Earth and Earendel is so massive that it warps light around it.
Earendel is thought to have formed roughly a billion years after the Big Bang, which itself was 13.8 billion years ago. NASA said: “The discoveries have opened a new realm of the universe to stellar physics, and new subject matter to scientists studying the early universe, where once galaxies were the smallest detectable cosmic objects.
 'Weird' comet heading towards the sun could be from another solar system
'Weird' comet heading towards the sun could be from another solar system
 Artist's impression of the James Webb Telescope (NASA / SWNS)
Artist's impression of the James Webb Telescope (NASA / SWNS)“The team has cautious hope this could be a step toward the detection of one of the very first generation of stars, composed only of the raw ingredients of the universe created in the big bang – hydrogen and helium.” While other features in the galaxy appear multiple times due to the gravitational lensing, Earendel only appears as a single point of light even in Webb’s high-resolution infrared imaging.
Based on this, astronomers determine the object is magnified by a factor of at least 4,000, and thus is extremely small - the most distant star ever detected, observed 1 billion years after the big bang. The previous record-holder for the most distant star was detected by Hubble and observed around 4 billion years after the big bang. Another research team using Webb recently identified a gravitationally lensed star they nicknamed Quyllur, a red giant star observed 3 billion years after the big bang.
Stars as massive as Earendel often have companions. Astronomers did not expect Webb to reveal any companions of Earendel since they would be so close together and indistinguishable on the sky. However, based solely on the colours of Earendel, astronomers think they see hints of a cooler, redder companion star. This light has been stretched by the expansion of the universe to wavelengths longer than Hubble’s instruments can detect, and so was only detectable with Webb.
Read more similar news:
Comments:
comments powered by Disqus